Traditional interpretation
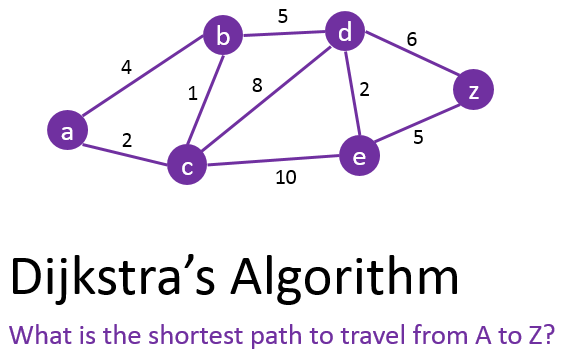
Dijkstra's algorithm (or Dijkstra's Shortest Path First algorithm, SPF algorithm)[2] is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a graph, which may represent, for example, road networks. It was conceived by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956 and published three years late
How neuromythography uses
🏚️
Dijkstra is a Brain Area
Dijkstra represents the mMB.
Notes
🗒️
Dijkstra invented an algorithm for finding the shortest path between two points.
mMB tracks head angular velocity during turns, and coarsely keeps track of bursts of fast and slow speed. These are chained together to find paths.
Partner with ventral tegmental nucleus (VTN) in theta rhythm.
Partner with lateral MB (head direction).
Output to DTN (Canopus) for determining waypoints.
mMB tracks head angular velocity during turns, and coarsely keeps track of bursts of fast and slow speed. These are chained together to find paths.
Partner with ventral tegmental nucleus (VTN) in theta rhythm.
Partner with lateral MB (head direction).
Output to DTN (Canopus) for determining waypoints.
Resources
Tributes
Member-submitted gallery images (free membership required to submit).